
|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
The sand battery is a new technology that promises a cheap and sustainable solution for storing energy from renewable sources such as the sun or wind. A sand battery uses sand or other silicate materials that are heated by electricity and store energy as heat. The heat can then be used for heating, industrial processes or converted back into electricity. The sand battery has several advantages such as low cost, long life, high capacity and minimal environmental impact. On the other hand, it also has some disadvantages such as low efficiency, large size, need for insulation and limited availability of silica resources. In this article, we present the principle and characteristics of the sand battery, its first implementation in Finland. Translated with DeepL.com (free version)
The principle and characteristics of the sand battery
The sand battery is based on the principle of thermal energy storage, which consists of storing energy in the form of heat in a material that has a high heat capacity. Thermal capacity is the ability of a material to absorb and release heat when the temperature changes. The higher the heat capacity, the more energy can be stored in the material. A sand battery uses sand or other silicate materials such as glass, ceramic or quartz, which have a high heat capacity and are cheap and available. The sand or other silica material is placed in a container that is insulated from the environment. The container is then connected to a source of electricity which heats the material by electrical resistance. This raises the temperature of the material to several hundred or thousand degrees Celsius. The heat is then retained in the material for several days, weeks or months, depending on the quality of the insulation. When the energy needs to be used, the heat can be released from the material either directly, for example for heating, or indirectly, for example by a heat engine that converts the heat into electricity.
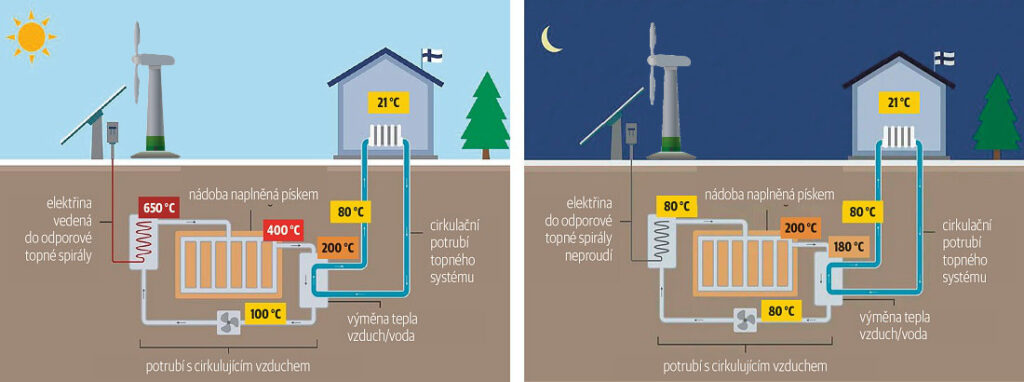
- Excess energy from renewable sources such as solar or wind power is used to heat the air using a resistance heater.
- The heated air is fed into a steel container filled with sand, where the heat is transferred to the sand via a heat exchanger.
- The sand is heated to temperatures of up to 1000 °C and retains heat for several months.
- When the stored energy needs to be used, the air is again pushed through the container and the heat from the sand is recovered.
- The thermal air is then fed into the heating system or into an electric generator.
Main advantages of the sand battery:
- Low price: Sand or other silicate materials are cheap and available, and therefore the sand battery is much cheaper than other types of batteries. For example, the cost of a sand battery is estimated at 0.5 to 2 euros per kWh, while the cost of a lithium-ion battery is about 100 to 200 euros per kWh.
- Long life: Sand or other silica materials are resistant to wear and degradation, and therefore the sand battery is able to operate for several decades without the need for maintenance or replacement. For example, the life of a sand battery is estimated at 40 to 50 years, while the life of a lithium-ion battery is about 10 to 15 years.
- High Capacity: Sand or other silicate materials have a high heat capacity, and therefore a sand battery is able to store a large amount of energy in a small volume. For example, the capacity of a sand battery is estimated at 1.5 to 2 kWh/kg, while the capacity of a lithium-ion battery is about 0.2 kWh/kg.
- Minimal environmental impact: Sand or other silicate materials are harmless to the environment, making the sand battery environmentally friendly and recyclable. The sand battery does not use any toxic or rare elements such as lithium, cobalt or nickel, which are used in other types of batteries and whose extraction and processing have a negative impact on the environment and human rights.
On the other hand, the sand battery also has some drawbacks that need to be overcome before it becomes a widely used energy storage technology. These disadvantages include:
- Low efficiency: A sand battery has low efficiency, which means that some energy is lost in the conversion from electricity to heat and back again. The efficiency of a sand battery is estimated at 25 to 50%, while the efficiency of a lithium-ion battery is about 80 to 90%. This means that a sand battery requires more energy to charge and provides less energy to discharge than other types of batteries. According to information from Polar Night Energy, they are able to create an efficiency of up to 95% in storing thermal energy.
- Large size: The sand faucet has a large size, which means it needs a lot of space for installation and operation. A sand battery consists of a container of sand or other silica material that is insulated and connected to an electricity source and a heat recovery system. Thus, a sand battery is similar in size to a container or small house, while other types of batteries are much smaller and more compact.
- Insulation needs: A sand battery needs good insulation to prevent heat loss from the material to the surroundings. The insulation must be able to withstand high temperatures while being lightweight and inexpensive.
První písková baterie postavená ve Finsku v roce 2023 společností Polar Night Energy ve spolupráci s malou elektrárnou ve městě Kankaanpää. Tato baterie je naplněna asi 100 tunami stavebního písku, který je zahříván až na 500 °C a slouží k vytápění jedné z městských čtvrtí. Tento projekt je prvním komerčním testem této technologie a ukazuje její možné aplikace a výzvy.
Research into alternative materials for the sand battery by the German university RWTH Aachen. This research explores the possibility of using glass, ceramics or quartz instead of sand, which could have higher thermal capacity, lower thermal conductivity and better mechanical properties. This research could improve the performance and durability of the sand battery.
Real application of DIY sand batteries in the Czech Republic:
Sources:
https://www.comsol.com/story/heating-buildings-with-solar-energy-stored-in-sand-105101
Přidejte odpověď
You must be logged in to post a comment.